Lorentz transformations.
Book by T. Matolcsi
Mathematical Preliminaries
A vector is represented as a nx1 matrix (column vector)
fricas
vect(x:List Expression Integer):Matrix Expression Integer == matrix map(y+->[y],x)
Function declaration vect : List(Expression(Integer)) -> Matrix(
Expression(Integer)) has been added to workspace.
Type: Void
fricas
vect [a0,a1,a2,a3]
fricas
Compiling function vect with type List(Expression(Integer)) ->
Matrix(Expression(Integer))Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Identity
fricas
ID:=diagonalMatrix([1,1,1,1])
Type: Matrix(Integer)
Verification
fricas
possible(x)==subst(x, map(y+->(y=(random(100) - random(100))),variables x) )
Type: Void
fricas
is?(eq:Equation EXPR INT):Boolean == (lhs(eq)-rhs(eq)=0)::Boolean
Function declaration is? : Equation(Expression(Integer)) -> Boolean
has been added to workspace.
Type: Void
fricas
Is?(eq:Equation(Matrix(EXPR(INT)))):Boolean == _
( (lhs(eq)-rhs(eq)) :: Matrix Expression AlgebraicNumber = _
zero(nrows(lhs(eq)),ncols(lhs(eq)))$Matrix Expression AlgebraicNumber )::Boolean
Function declaration Is? : Equation(Matrix(Expression(Integer))) ->
Boolean has been added to workspace.
Type: Void
Lorentz Form (metric)
fricas
G:=diagonalMatrix [-1,1,1,1]
Type: Matrix(Integer)
applied to a vector produces a co-vector (represent as a 1xn matrix or row vector)
fricas
g(x) == transpose(x)*G
Type: Void
fricas
g(vect [a0,a1,a2,a3])
fricas
Compiling function g with type Matrix(Expression(Integer)) -> Matrix
(Expression(Integer))Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Scalar product
fricas
dot(x,y) == (g(x)*y)::Expression Integer
Type: Void
fricas
dot(vect [a0,a1,a2,a3], vect [b0,b1,b2,b3])
fricas
Compiling function dot with type (Matrix(Expression(Integer)),Matrix
(Expression(Integer))) -> Expression(Integer)
Type: Expression(Integer)
Tensor product
fricas
tensor(x,y) == x*g(y)
Type: Void
fricas
tensor(vect [a0,a1,a2,a3], vect [b0,b1,b2,b3])
fricas
Compiling function tensor with type (Matrix(Expression(Integer)),
Matrix(Expression(Integer))) -> Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Massive Objects
A material object (also referred to as an observer) is represented by a
time-like 4-vector
fricas
P:=vect [sqrt(p1^2+p2^2+p3^2+1),-p1,-p2,-p3];
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
dot(P,P)
Type: Expression(Integer)
fricas
Q:=vect [sqrt(q1^2+q2^2+q3^2+1),-q1,-q2,-q3];
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
R:=vect [sqrt(r1^2+r2^2+r3^2+1),-r1,-r2,-r3];
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
S:=1/sqrt(1-s1^2-s2^2-s3^2)*vect [1,-s1,-s2,-s3]
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
dot(S,S)
Type: Expression(Integer)
fricas
T:=1/sqrt(1-t1^2-t2^2-t3^2)*vect [1,-t1,-t2,-t3]
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Observer "at rest"
fricas
vect [1,0,0,0]
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
dot(%,%)
Type: Expression(Integer)
Associated with each such vector is the orthogonal 3-d Euclidean subspace
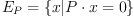
Relative Velocity
An object P has a unique relative velocity w(P,Q) with respect
to object Q given by
fricas
v(P,Q)==-P/dot(P,Q)-Q
Type: Void
Observer P measures velocity v(Q,P). v(Q,P) is space-like
fricas
dot(v(P,vect [1,0,0,0]),v(P,vect [1,0,0,0]))
fricas
Compiling function v with type (Matrix(Expression(Integer)),Matrix(
Expression(Integer))) -> Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Type: Expression(Integer)
and in 
fricas
dot(P,v(Q,P))
Type: Expression(Integer)
fricas
possible dot(v(Q,P),v(Q,P))::EXPR Float
fricas
Compiling function possible with type Expression(Integer) ->
Expression(Integer)Type: Expression(Float)
fricas
dot(Q,v(P,Q))
Type: Expression(Integer)
fricas
possible dot(v(P,Q),v(P,Q))::EXPR Float
Type: Expression(Float)
Velocity with respect to observer "at rest"
fricas
v(vect [u0,u1,u2,u3],vect [1,0,0,0])
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
v(R,vect [1,0,0,0])
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
v(S,vect [1,0,0,0])
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Non-reciprocal velocities
fricas
v(vect [1,0,0,0],S)
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
v(vect [1,0,0,0],R)
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
is?(dot(v(P,Q),v(P,Q))=dot(v(Q,P),v(Q,P)))
fricas
Compiling function is? with type Equation(Expression(Integer)) ->
BooleanType: Boolean
Lorentz Boost
is a linear bijection  that preserves
that preserves
 and maps orthogonal compliments into each other.
and maps orthogonal compliments into each other.
fricas
L(P,Q) == ID + tensor(P+Q,P+Q)/(1-dot(P,Q)) - 2*tensor(P,Q)
Type: Void
fricas
Is?(L(P,P) = ID)
fricas
Compiling function L with type (Matrix(Expression(Integer)),Matrix(
Expression(Integer))) -> Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
Compiling function Is? with type Equation(Matrix(Expression(Integer)
)) -> BooleanType: Boolean
fricas
Is?(L(P,Q)*L(Q,P) = ID)
Type: Boolean
fricas
Is?(L(P,Q)*Q=P)
Type: Boolean
fricas
Is?(L(P,Q)*v(P,Q) = -v(Q,P))
Type: Boolean
Composition of two Lorentz boosts is not a Lorentz boost
unless all three observers are in the same plane.
fricas
Is?(L(R,P)*L(P,Q) = L(R,Q))
Type: Boolean
fricas
RQ:=a*R+b*Q;
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
rq:=solve(dot(RQ,RQ)=-1,b); #rq
fricas
RQ1:=eval(RQ,rq.1);
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
dot(RQ1,RQ1)
Type: Expression(Integer)
fricas
Is?(L(R,RQ1)*L(RQ1,Q) = L(R,Q))
Type: Boolean
fricas
RQ2:=eval(RQ,rq.2);
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
Is?(RQ1=RQ2)
Type: Boolean
fricas
dot(RQ2,RQ2)
Type: Expression(Integer)
fricas
Is?(L(R,RQ2)*L(RQ2,Q) = L(R,Q))
Type: Boolean
but the composition does preserve observers and magnitudes
fricas
LRPQ := L(R,P)*L(P,Q);
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
Is?(LRPQ*Q = L(R,Q)*Q)
Type: Boolean
fricas
is?(dot(LRPQ*v(S,Q),LRPQ*v(S,Q))=dot(L(R,Q)*v(S,Q),L(R,Q)*v(S,Q)))
Type: Boolean
Lorentz boost with respect to observer "at rest"
fricas
LT:=L(vect [1,0,0,0],vect [u0,-u1,-u2,-u3])
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
Two dimensional Lorentz Transformation
fricas
matrix [[1/sqrt(1-v'^2),v'/sqrt(1-v'^2),0,0],[v'/sqrt(1-v'^2),1/sqrt(1-v'^2),0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]]
Type: Matrix(Expression(Integer))
fricas
Is?(%=map(x+->eval(x,[u0=1/sqrt(1-v'^2),u1=v'/sqrt(1-v'^2),u2=0,u3=0]),LT))
Type: Boolean





![]()
![]()




![]() that preserves
that preserves
![]() and maps orthogonal compliments into each other.
and maps orthogonal compliments into each other.

