The Algebra of Complex Numbers Is Frobenius In Many Ways
Linear operators over a 2-dimensional vector space representing the algebra of complex numbers
Ref:
We need the Axiom LinearOperator library.
fricas
(1) -> )library CARTEN ARITY CMONAL CPROP CLOP CALEY
CartesianTensor is now explicitly exposed in frame initial
CartesianTensor will be automatically loaded when needed from
/var/aw/var/LatexWiki/CARTEN.NRLIB/CARTEN
Arity is now explicitly exposed in frame initial
Arity will be automatically loaded when needed from
/var/aw/var/LatexWiki/ARITY.NRLIB/ARITY
ClosedMonoidal is now explicitly exposed in frame initial
ClosedMonoidal will be automatically loaded when needed from
/var/aw/var/LatexWiki/CMONAL.NRLIB/CMONAL
ClosedProp is now explicitly exposed in frame initial
ClosedProp will be automatically loaded when needed from
/var/aw/var/LatexWiki/CPROP.NRLIB/CPROP
>> System error:
The value
11131
is not of type
LIST
Use the following macros for convenient notation
fricas
-- summation
macro Σ(x,i,n)==reduce(+,[x for i in n])
Type: Void
fricas
-- list
macro Ξ(f,i,n)==[f for i in n]
Type: Void
fricas
-- subscript and superscripts
macro sb == subscript
Type: Void
fricas
macro sp == superscript
Type: Void
𝐋 is the domain of 2-dimensional linear operators over the rational functions ℚ (Expression Integer), i.e. ratio of polynomials with integer coefficients.
fricas
dim:=2
fricas
macro ℒ == List
Type: Void
fricas
macro ℂ == CaleyDickson
Type: Void
fricas
macro ℚ == Expression Integer
Type: Void
fricas
𝐋 := ClosedLinearOperator(OVAR ['1,'i], ℚ)
There are no library operations named ClosedLinearOperator
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op ClosedLinearOperator
to learn if there is any operation containing "
ClosedLinearOperator " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named
ClosedLinearOperator with argument type(s)
Type
Type
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Now generate structure constants for Complex Algebra
The basis consists of the real and imaginary units. We use complex multiplication to form the "multiplication table" as a matrix. Then the structure constants can be obtained by dividing each matrix entry by the list of basis vectors.
Split-complex can be specified by Caley-Dickson parameter (i2)
fricas
--i2:=sp('i,[2])
i2:= -1 -- complex
Type: Integer
fricas
QQ := ℂ(ℚ,'i,-i2);
There are no library operations named CaleyDickson
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op CaleyDickson
to learn if there is any operation containing " CaleyDickson " in
its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named
CaleyDickson with argument type(s)
Type
Variable(i)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Basis: Each B.i is a complex number
fricas
B:ℒ QQ := map(x +-> hyper x,1$SQMATRIX(dim,ℚ)::ℒ ℒ ℚ)
QQ is not a valid type.
Units
fricas
e:=𝐞.1; i:=𝐞.2;
There are no library operations named 𝐞
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐞
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐞 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐞
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Multiplication of arbitrary ccomplex numbers 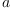 and
and 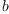
fricas
a:=Σ(sb('a,[i])*𝐞.i, i,1..dim)
There are no library operations named 𝐞
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐞
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐞 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐞
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
FriCAS will attempt to step through and interpret the code.
There are no library operations named 𝐞
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐞
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐞 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐞
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Multiplication is Associative
fricas
test(
( I Y ) / _
( Y ) = _
( Y I ) / _
( Y ) )
There are no exposed library operations named I but there is one
unexposed operation with that name. Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)display op I
to learn more about the available operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named I
with argument type(s)
Variable(Y)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
A scalar product is denoted by the (2,0)-tensor
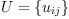
fricas
U:=Σ(Σ(script('u,[[],[i,j]])*𝐝.i*𝐝.j, i,1..dim), j,1..dim)
There are no library operations named 𝐝
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐝
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐝 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐝
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
FriCAS will attempt to step through and interpret the code.
There are no library operations named 𝐝
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐝
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐝 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐝
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Definition 1
We say that the scalar product is associative if the tensor
equation holds:
Y = Y
U U
In other words, if the (3,0)-tensor:
(three-point function) is zero.
Using the LinearOperator domain in Axiom and some carefully chosen symbols we can easily enter expressions that are both readable and interpreted by Axiom as "graphical calculus" diagrams describing complex products and compositions of linear operators.
fricas
ω:𝐋 :=
( Y I ) /
U -
( I Y ) /
U
𝐋 is not a valid type.
Definition 2
An algebra with a non-degenerate associative scalar product
is called a [Frobenius Algebra]?.
The Cartan-Killing Trace
fricas
Ú:=
( Y Λ ) / _
( Y I ) / _
V
There are no exposed library operations named Y but there are 2
unexposed operations with that name. Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)display op Y
to learn more about the available operations.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named Y
with argument type(s)
Variable(Λ)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
forms a non-degenerate associative scalar product for Y
fricas
Ũ := Ù
Type: Variable(Ù)
fricas
test
( Y I ) /
Ũ =
( I Y ) /
Ũ
There are no exposed library operations named Y but there are 2
unexposed operations with that name. Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)display op Y
to learn more about the available operations.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named Y
with argument type(s)
Variable(I)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
General Solution
We may consider the problem where multiplication Y is given,
and look for all associative scalar products 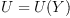
This problem can be solved using linear algebra.
fricas
)expose MCALCFN
MultiVariableCalculusFunctions is now explicitly exposed in frame
initial
J := jacobian(ravel ω,concat map(variables,ravel U)::ℒ Symbol);
There are 1 exposed and 0 unexposed library operations named ravel
having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op ravel
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named ravel
with argument type(s)
Variable(ω)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
The matrix J transforms the coefficients of the tensor 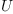 into coefficients of the tensor
into coefficients of the tensor 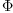 . We are looking for
the general linear family of tensors
. We are looking for
the general linear family of tensors 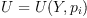 such that
such that
J transforms 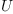 into
into 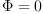 for any such
for any such 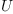 .
.
If the null space of the J matrix is not empty we can use
the basis to find all non-trivial solutions for U:
fricas
Ñ:=nullSpace(J)
There are 3 exposed and 3 unexposed library operations named
nullSpace having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be
applicable. Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op nullSpace
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named
nullSpace with argument type(s)
Variable(J)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
This defines a family of pre-Frobenius algebras:
fricas
zero? eval(ω,ℰ)
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Variable(ω)
Variable(ℰ)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Frobenius Form (co-unit)
fricas
d:=ε1*𝐝.1+εi*𝐝.2
There are no library operations named 𝐝
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐝
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐝 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐝
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Express scalar product in terms of Frobenius form
fricas
𝔓:=solve(𝔇,Ξ(sb('p,[i]), i,1..#Ñ)).1
There are 2 exposed and 2 unexposed library operations named #
having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op #
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named #
with argument type(s)
Variable(Ñ)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
In general the pairing is not symmetric!
fricas
u1:=matrix Ξ(Ξ(retract((𝐞.i 𝐞.j)/Ų), i,1..dim), j,1..dim)
There are no library operations named 𝐞
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐞
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐞 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐞
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
FriCAS will attempt to step through and interpret the code.
There are no library operations named 𝐞
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op 𝐞
to learn if there is any operation containing " 𝐞 " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named 𝐞
with argument type(s)
PositiveInteger
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
The scalar product must be non-degenerate:
fricas
Ů:=determinant u1
There are 3 exposed and 1 unexposed library operations named
determinant having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be
applicable. Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op determinant
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named
determinant with argument type(s)
Variable(u1)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Cartan-Killing is a special case
fricas
ck:=solve(equate(eval(Ũ,𝔓)=Ų),[ε1,εi]).1
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Variable(Ù)
Variable(𝔓)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Frobenius scalar product of complex numbers 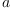 and
and 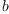
fricas
a:=sb('a,[1])*e+sb('a,[2])*i
Type: Polynomial(Integer)
fricas
b:=sb('b,[1])*e+sb('b,[2])*i
Type: Polynomial(Integer)
fricas
(a,a)/Ų
There are 12 exposed and 15 unexposed library operations named /
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op /
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named /
with argument type(s)
Tuple(Polynomial(Integer))
Variable(Ų)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Definition 3
Co-scalar product
Solve the Snake Relation as a system of linear equations.
fricas
Ω:𝐋:=Σ(Σ(script('u,[[i,j]])*𝐞.i*𝐞.j, i,1..dim), j,1..dim)
𝐋 is not a valid type.
The common demoninator is 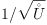
fricas
squareFreePart((factor denom Ů)::ℚ) / squareFreePart((factor numer Ů)::ℚ)
There are 3 exposed and 3 unexposed library operations named denom
having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op denom
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named denom
with argument type(s)
Variable(Ů)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Check "dimension" and the snake relations.
fricas
O:𝐋:=
Ω /
Ų
𝐋 is not a valid type.
Cartan-Killing co-scalar
fricas
eval(Ω,ck)
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Variable(Ω)
Variable(ck)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Definition 4
Co-algebra
Compute the "three-point" function and use it to define co-multiplication.
fricas
W:=
(Y I) /
Ų
There are no exposed library operations named Y but there are 2
unexposed operations with that name. Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)display op Y
to learn more about the available operations.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named Y
with argument type(s)
Variable(I)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Cartan-Killing co-multiplication
fricas
eval(λ,ck)
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Variable(λ)
Variable(ck)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
fricas
test
( I ΩX ) /
( Y I ) = λ
There are no exposed library operations named I but there is one
unexposed operation with that name. Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)display op I
to learn more about the available operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named I
with argument type(s)
Variable(ΩX)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Co-associativity
fricas
test(
( λ ) / _
( I λ ) = _
( λ ) / _
( λ I ) )
There are no exposed library operations named I but there is one
unexposed operation with that name. Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)display op I
to learn more about the available operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named I
with argument type(s)
Variable(λ)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
fricas
test
e /
λ = ΩX
Type: Boolean
Frobenius Condition (fork)
fricas
H :=
Y /
λ
Type: Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
fricas
test
( λ I ) /
( I Y ) = H
There are no library operations named λ
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op λ
to learn if there is any operation containing " λ " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named λ
with argument type(s)
Variable(I)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
The Cartan-Killing form makes H of the Frobenius condition idempotent
fricas
test( eval(H,ck)=eval(H/H,ck) )
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
Variable(ck)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
And it is unique.
fricas
h1:=map(numer,ravel(H-H/H)::List FRAC POLY INT);
There are 1 exposed and 0 unexposed library operations named ravel
having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op ravel
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named ravel
with argument type(s)
Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Handle
fricas
Φ :=
λ /
Y
Type: Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
The Cartan-Killing form makes Φ of the identity
fricas
test( eval(Φ,ck)=I )
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
Variable(ck)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
and it can be the identity in only this one way.
fricas
solve(equate(Φ=I),[ε1,εi])
There are no library operations named equate
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op equate
to learn if there is any operation containing " equate " in its
name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named
equate with argument type(s)
Equation(Fraction(Polynomial(Integer)))
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
If handle is identity then fork is idempotent but the converse is not true
fricas
Φ1:=map(numer,ravel(Φ-I)::List FRAC POLY INT);
There are 1 exposed and 0 unexposed library operations named ravel
having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op ravel
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named ravel
with argument type(s)
Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Figure 12
fricas
φφ:= _
( Ω Ω ) / _
( X I I ) / _
( I X I ) / _
( I I X ) / _
( Y Y );
There are no library operations named Ω
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op Ω
to learn if there is any operation containing " Ω " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named Ω
with argument type(s)
Variable(Ω)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
For Cartan-Killing this is just the co-scalar
fricas
test(eval(φφ,ck)=eval(Ω,ck))
There are 10 exposed and 6 unexposed library operations named eval
having 2 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op eval
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named eval
with argument type(s)
Variable(φφ)
Variable(ck)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
Bi-algebra conditions
fricas
ΦΦ:= _
( λ λ ) / _
( I I X ) / _
( I X I ) / _
( I I X ) / _
( Y Y ) ;
There are no library operations named λ
Use HyperDoc Browse or issue
)what op λ
to learn if there is any operation containing " λ " in its name.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named λ
with argument type(s)
Variable(λ)
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
The Cartan Killing form is a bi-algebra
fricas
bi1:=map(numer,ravel(ΦΦ-H)::List FRAC POLY INT);
There are 1 exposed and 0 unexposed library operations named ravel
having 1 argument(s) but none was determined to be applicable.
Use HyperDoc Browse, or issue
)display op ravel
to learn more about the available operations. Perhaps
package-calling the operation or using coercions on the arguments
will allow you to apply the operation.
Cannot find a definition or applicable library operation named ravel
with argument type(s)
Fraction(Polynomial(Integer))
Perhaps you should use "@" to indicate the required return type,
or "$" to specify which version of the function you need.
(2.2,0.1)(2.6,0.1)(2.6,0.9)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](2.4,0.3)(2.4,-0.1)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](2.4,-0.1)(2.4,-0.9)(3.0,-0.9)(3.0,-0.1)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](3.0,-0.1)(3.0,0.9)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](4.8,0.9)(4.8,0.1)(4.4,0.1)(4.4,0.9)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](4.6,0.3)(4.6,-0.1)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](4.6,-0.1)(4.6,-0.9)(4.0,-0.9)(4.0,-0.1)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](4.0,-0.1)(4.0,0.9)
\usefont{T1}{ptm}{m}{n}
\rput(3.4948437,0.205){-}
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](0.6,-0.7)(0.6,0.9)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](0.0,-0.1)(0.0,-0.9)(1.2,-0.9)(1.2,-0.1)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](0.0,-0.1)(0.0,0.9)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](1.2,-0.1)(1.2,0.9)
\usefont{T1}{ptm}{m}{n}
\rput(1.6948438,0.205){=}
\end{pspicture}
}
\scalebox{1} % Change this value to rescale the drawing.
{
\begin{pspicture}(0,-0.92)(4.82,0.92)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](2.2,0.9)(2.2,0.1)(2.6,0.1)(2.6,0.9)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](2.4,0.3)(2.4,-0.1)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](2.4,-0.1)(2.4,-0.9)(3.0,-0.9)(3.0,-0.1)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](3.0,-0.1)(3.0,0.9)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](4.8,0.9)(4.8,0.1)(4.4,0.1)(4.4,0.9)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](4.6,0.3)(4.6,-0.1)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](4.6,-0.1)(4.6,-0.9)(4.0,-0.9)(4.0,-0.1)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](4.0,-0.1)(4.0,0.9)
\usefont{T1}{ptm}{m}{n}
\rput(3.4948437,0.205){-}
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](0.6,-0.7)(0.6,0.9)
\psbezier[linewidth=0.04](0.0,-0.1)(0.0,-0.9)(1.2,-0.9)(1.2,-0.1)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](0.0,-0.1)(0.0,0.9)
\psline[linewidth=0.04cm](1.2,-0.1)(1.2,0.9)
\usefont{T1}{ptm}{m}{n}
\rput(1.6948438,0.205){=}
\end{pspicture}
}](images/2375189246716000159-16.0px.png)