|
|
|
last edited 18 years ago by Bill Page |
Edit detail for SandBoxComplementsdalgebrelineaire revision 7 of 9
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | ||
|
Editor: Bill Page
Time: 2008/01/18 13:57:36 GMT-8 |
||
| Note: missing ) in projortho X | ||
added:
\begin{axiom}
---
--- linalg.input
--- Francois Maltey - janvier 2008
---
---
--- A partir de rowEchelon
---
sameSizeVectors? Lb ==
null Lb => true
n := #(first Lb)
every? (t +-> #t=n, rest Lb)
basis mat ==
mat2 := rowEchelon mat
basis := []
indrow : Integer := 1
n : Integer := ncols mat
m : Integer := nrows mat
for k in 1..n repeat
if indrow <= m and mat2.(indrow,k) ~= 0
then
basis := cons (column (mat, k), basis)
indrow := indrow + 1
reverse basis
basisLV Lv ==
null Lv => []
not (sameSizeVectors? Lv) => error "vectors have not the same size"
basis transpose matrix Lv
basisMat mat == basis mat
sumBasisLLV LLv == basisLV concat LLv
sumBasis2 (Lv1, Lv2) == basisLV concat (Lv1, Lv2)
kernelMat mat ==
lv := nullSpace mat
#lv = 1 and lv.1 = 0*lv.1 => []
lv
subVector (v, a, b) == vector (elt (entries v, a..b))
linearVector (t, Lv) == reduce (+, [t.i*Lv.i for i in 1..#t])
intBasis2 (Lv1, Lv2) ==
Lb1 := basisLV Lv1
Lb2 := basisLV Lv2
null Lb1 => []
null Lb2 => []
#(first Lb1) ~= #(first Lb2) => error "vectors have not the same size"
lkv := kernelMat transpose matrix concat (Lb2, Lb1)
d1 := #Lb1
d2 := #Lb2
LcoeffV1 := [subVector (kv, d2+1, d1+d2) for kv in lkv]
[linearVector (cc, Lb1) for cc in LcoeffV1]
intBasisLLV LLv ==
#LLv = 0 => error "no space to intersect"
#LLv = 1 => LLv.1
--reduce (intBasis2, LLv)
intBasis2 (LLv.1, intBasisLLV rest LLv)
\end{axiom}
\begin{axiom}
---
--- inversegeneralisee.input
--- Francois Maltey - janvier 2008
---
--- inverse generalisee
---
--- a partir du livre Algebre lineaire par Joseph Grifone p.375
--- applique pas à pas la méthode du livre à l'exemple
A := matrix [[2,1,-1,1],[1,1,0,1],[3,2,-1,2]]
--- kerA est une base de ker f ou f est definie par la matrice A
KerA := kernelMat A
--- Le noyau de la matrice dont les lignes sont des vecteurs generateurs
--- d'un sev est le sev orthogonal. C'est un sous-espace supplementaire.
--- baseF est une base d'un sous-espace supplémentaire de ker f
baseF := kernelMat matrix KerA
--- les vecteurs colonnes de A engendre l'image Im f.
--- baseImA est une base de l'image de f calculee a partir de la matrice A
baseImA := basis A
--- baseG et baseG2 sont deux bases d'un sous-espace supplementaire de Im f
--- l'une calculee a partir de la matrice A, l'autre d'une base de Im f.
baseG := kernelMat transpose A
baseG2:= kernelMat matrix baseImA
--- La restriction g de f est un isomorphisme du supplementaire F de ker f
--- dans Im f. La matrice de g dans les bases de F et de Im f est obtenue
--- en decomposant dans Im f les images des vecteurs de la base de F.
--- La commande particularSolution effectue cette decomposition.
MP := transpose matrix baseImA
map (X +-> A*X, baseF)
map (X +-> particularSolution (MP, A*X), baseF)
B := transpose matrix map (X +-> particularSolution (MP, A*X), baseF)
--- La matrice C est celle de l'isomorphisme reciproque dans ces bases.
C := B^-1
--- la projection orthogonale de E' sur Im f peut être obtenue
--- à partir d'une base orthonormee de Im f.
--- baseImA est une base de Im f, la fonction gramschmidt construit
--- la bon associee.
GS := gramschmidt (baseImA::List Vector Expression Integer)
bonImA := map (M +-> column (M, 1), GS)
projortho X ==
reduce (+, map (V +-> dot (V, X::Vector Expression Integer) * V, bonImA))
--- exemple de projection orthogonale sur Im f.
projortho vector [1,2,4]
--- construction de la composition g^-1 o p de E' dans E
--- en calculant les images des vecteurs de la base canonique de E'
--- puis passage des coordonnees de g^-1 o p de la base de F
--- à la base canonique de E.
Id3 := diagonalMatrix [1 for i in 1..3]
RES1 := [projortho column (Id3, i) for i in 1..3]
RES2 := [X::Vector Fraction Integer for X in RES1]
RES3 := [particularSolution (MP, X) for X in RES2]
RES := [C * X for X in RES3::List Vector Fraction Integer]
AA := transpose matrix baseF * transpose matrix RES
--- vérifications de quelques propriétés : A AA A = A et AA A AA = AA
--- transpose (A AA) = A AA : car les sev choisis sont des orthogonaux
AA * A * AA - AA
A * AA * A - A
transpose (AA * A) - AA * A
transpose (A * AA) - A * AA
\end{axiom}
| Download: pdf dvi ps src tex log |

axiom--- --- linalg.input --- Francois Maltey - janvier 2008 --- --- --- A partir de rowEchelon --- sameSizeVectors? Lb == null Lb => true n := #(first Lb) every? (t +-> #t=n, rest Lb)
Type: Void
axiombasis mat == mat2 := rowEchelon mat basis := [] indrow : Integer := 1 n : Integer := ncols mat m : Integer := nrows mat for k in 1..n repeat if indrow <= m and mat2.(indrow,k) ~= 0 then basis := cons (column (mat, k), basis) indrow := indrow + 1 reverse basis
Type: Void
axiombasisLV Lv == null Lv => [] not (sameSizeVectors? Lv) => error "vectors have not the same size" basis transpose matrix Lv
Type: Void
axiombasisMat mat == basis mat
Type: Void
axiomsumBasisLLV LLv == basisLV concat LLv
Type: Void
axiomsumBasis2 (Lv1, Lv2) == basisLV concat (Lv1, Lv2)
Type: Void
axiomkernelMat mat == lv := nullSpace mat #lv = 1 and lv.1 = 0*lv.1 => [] lv
Type: Void
axiomsubVector (v, a, b) == vector (elt (entries v, a..b))
Type: Void
axiomlinearVector (t, Lv) == reduce (+, [t.i*Lv.i for i in 1..#t])
Type: Void
axiomintBasis2 (Lv1, Lv2) == Lb1 := basisLV Lv1 Lb2 := basisLV Lv2 null Lb1 => [] null Lb2 => [] #(first Lb1) ~= #(first Lb2) => error "vectors have not the same size" lkv := kernelMat transpose matrix concat (Lb2, Lb1) d1 := #Lb1 d2 := #Lb2 LcoeffV1 := [subVector (kv, d2+1, d1+d2) for kv in lkv] [linearVector (cc, Lb1) for cc in LcoeffV1]
Type: Void
axiomintBasisLLV LLv == #LLv = 0 => error "no space to intersect" #LLv = 1 => LLv.1 --reduce (intBasis2, LLv) intBasis2 (LLv.1, intBasisLLV rest LLv)
Type: Void
axiom--- --- inversegeneralisee.input --- Francois Maltey - janvier 2008 --- --- inverse generalisee --- --- a partir du livre Algebre lineaire par Joseph Grifone p.375 --- applique pas à pas la méthode du livre à l'exemple A := matrix [[2,1,-1,1],[1,1,0,1],[3,2,-1,2]]
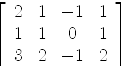 | (1) |
Type: Matrix Integer
axiom--- kerA est une base de ker f ou f est definie par la matrice A KerA := kernelMat A
axiom
Compiling function kernelMat with type Matrix Integer -> List Vector
Integer| (2) |
Type: List Vector Integer
axiom--- Le noyau de la matrice dont les lignes sont des vecteurs generateurs --- d'un sev est le sev orthogonal. C'est un sous-espace supplementaire. --- baseF est une base d'un sous-espace supplémentaire de ker f baseF := kernelMat matrix KerA
| (3) |
Type: List Vector Integer
axiom--- les vecteurs colonnes de A engendre l'image Im f. --- baseImA est une base de l'image de f calculee a partir de la matrice A baseImA := basis A Function definition for basis is being overwritten. The type of the local variable basis has changed in the computation. We will attempt to interpret the code. Compiled code for basis has been cleared.
| (4) |
Type: List Vector Integer
axiom--- baseG et baseG2 sont deux bases d'un sous-espace supplementaire de Im f --- l'une calculee a partir de la matrice A, l'autre d'une base de Im f. baseG := kernelMat transpose A
| (5) |
Type: List Vector Integer
axiombaseG2:= kernelMat matrix baseImA
| (6) |
Type: List Vector Integer
axiom--- La restriction g de f est un isomorphisme du supplementaire F de ker f --- dans Im f. La matrice de g dans les bases de F et de Im f est obtenue --- en decomposant dans Im f les images des vecteurs de la base de F. --- La commande particularSolution effectue cette decomposition. MP := transpose matrix baseImA
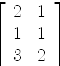 | (7) |
Type: Matrix Integer
axiommap (X +-> A*X, baseF)
| (8) |
Type: List Vector Integer
axiommap (X +-> particularSolution (MP, A*X), baseF)
| (9) |
Type: List Union(Vector Fraction Integer,"failed")
axiomB := transpose matrix map (X +-> particularSolution (MP, A*X), baseF)
| (10) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer
axiom--- La matrice C est celle de l'isomorphisme reciproque dans ces bases. C := B^-1
| (11) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer
axiom--- la projection orthogonale de E' sur Im f peut être obtenue --- à partir d'une base orthonormee de Im f. --- baseImA est une base de Im f, la fonction gramschmidt construit --- la bon associee. GS := gramschmidt (baseImA::List Vector Expression Integer)
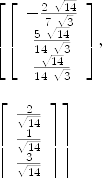 | (12) |
Type: List Matrix Expression Integer
axiombonImA := map (M +-> column (M, 1), GS)
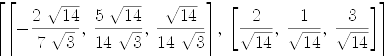 | (13) |
Type: List Vector Expression Integer
axiomprojortho X == reduce (+, map (V +-> dot (V, X::Vector Expression Integer) * V, bonImA))
Type: Void
axiom--- exemple de projection orthogonale sur Im f. projortho vector [1,2,4]
axiom
Compiling function projortho with type Vector PositiveInteger ->
Vector Expression Integer| (14) |
Type: Vector Expression Integer
axiom--- construction de la composition g^-1 o p de E' dans E --- en calculant les images des vecteurs de la base canonique de E' --- puis passage des coordonnees de g^-1 o p de la base de F --- à la base canonique de E. Id3 := diagonalMatrix [1 for i in 1..3]
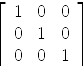 | (15) |
Type: Matrix Integer
axiomRES1 := [projortho column (Id3, i) for i in 1..3]
axiom
Compiling function projortho with type Vector Integer -> Vector
Expression Integer| (16) |
Type: List Vector Expression Integer
axiomRES2 := [X::Vector Fraction Integer for X in RES1]
| (17) |
Type: List Vector Fraction Integer
axiomRES3 := [particularSolution (MP, X) for X in RES2]
| (18) |
Type: List Union(Vector Fraction Integer,"failed")
axiomRES := [C * X for X in RES3::List Vector Fraction Integer]
| (19) |
Type: List Vector Fraction Integer
axiomAA := transpose matrix baseF * transpose matrix RES
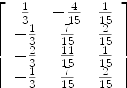 | (20) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer
axiom--- vérifications de quelques propriétés : A AA A = A et AA A AA = AA --- transpose (A AA) = A AA : car les sev choisis sont des orthogonaux AA * A * AA - AA
 | (21) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer
axiomA * AA * A - A
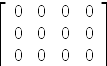 | (22) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer
axiomtranspose (AA * A) - AA * A
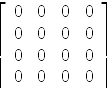 | (23) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer
axiomtranspose (A * AA) - A * AA
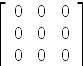 | (24) |
Type: Matrix Fraction Integer