Edit detail for GraphViz revision 1 of 18
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | ||
|
Editor: page
Time: 2007/09/19 01:22:14 GMT-7 |
||
| Note: | ||
changed: - "An Introduction to GraphViz":http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7275 By Mihalis Tsoukalos on Wed, 2004-09-08 23:00. How to use command-line tools and basic GraphViz utilities to produce graphs both simple and complex. GraphViz is a collection of tools for manipulating graph structures and generating graph layouts. Graphs can be either directed or undirected. GraphViz offers both graphical and command-line tools. A Perl interface also is available, but it is not covered here for reasons of generality. Graphical tools are not going to be discussed in this article either. Instead, this article focuses on using GraphViz from the command line. See more here: http://www.wickle.com/wikis/index.php/Graphviz_extension <hr /> The format of a GraphViz command is:: \\begin{latex} \\digraph[Options]{Name}{Specification} \\end{latex} Replace 'Options' with something like 'scale=1.0' and 'Specifications' with the actual graph, e.g. 'a->b; b->c'. Replace 'Name' with a name for your graph. The LaTeX extension for GraphViz (see: LatexTemplate) produces files named 'Name.dot' and 'Name.ps' in the images working directory. Since this graph name is global, it is a good idea to prefix the name with the name of the page on which the graph occurs. The follow graphs are generated by MathAction My First Graph:: !\begin{latex} \psfrag{alpha}[cc][cc]{$\alpha$} \psfrag{beta}[cc][cc]{$\beta$} \psfrag{gamma}[cc][cc]{$\gamma$} \digraph[scale=0.75]{GraphVizGraph1a}{rankdir=LR; alpha->beta; beta->gamma} \end{latex} Produces: \begin{latex} \psfrag{alpha}[cc][cc]{$\alpha$} \psfrag{beta}[cc][cc]{$\beta$} \psfrag{gamma}[cc][cc]{$\gamma$} \digraph[scale=0.75]{GraphVizGraph1a}{rankdir=LR; alpha->beta; beta->gamma} \end{latex} A More Complex Example:: \\begin{latex} \\digraph[scale=0.8]{GraphVizGraph2a}{ size ="4,4"; main [shape=box]; /* this is a comment */ main -> parse [weight=8]; parse -> execute; main -> init [style=dotted]; main -> cleanup; execute -> { make_string; printf} init -> make_string; edge [color=red]; main -> printf [style=bold,label="100 times"]; make_string [label="make a string"]; node [shape=box,style=filled,color=".7 .3 1.0"]; execute -> compare; } \\end{latex} Produces: \begin{latex} \digraph[scale=0.8]{GraphVizGraph2a}{ size ="4,4"; main [shape=box]; /* this is a comment */ main -> parse [weight=8]; parse -> execute; main -> init [style=dotted]; main -> cleanup; execute -> { make_string; printf} init -> make_string; edge [color=red]; main -> printf [style=bold,label="100 times"]; make_string [label="make a string"]; node [shape=box,style=filled,color=".7 .3 1.0"]; execute -> compare; } \end{latex} Here's One From http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7275 This:: \\begin{latex} \\digraph{GraphVizGraph3a} { node [shape = record]; node0 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> J | <f2> "]; node1 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> E | <f2> "]; node4 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> C | <f2> "]; node6 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> I | <f2> "]; node2 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> U | <f2> "]; node5 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> N | <f2> "]; node9 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> Y | <f2> "]; node8 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> W | <f2> "]; node10 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> Z | <f2> "]; node7 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> A | <f2> "]; node3 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> G | <f2> "]; "node0":f0 -> "node1":f1; "node0":f2 -> "node2":f1; "node1":f0 -> "node4":f1; "node1":f2 -> "node6":f1; "node4":f0 -> "node7":f1; "node4":f2 -> "node3":f1; "node2":f0 -> "node5":f1; "node2":f2 -> "node9":f1; "node9":f0 -> "node8":f1; "node9":f2 -> "node10":f1; } \\end{latex} Gets you this: \begin{latex} \digraph{GraphVizGraph3a} { node [shape = record]; node0 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> J | <f2> "]; node1 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> E | <f2> "]; node4 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> C | <f2> "]; node6 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> I | <f2> "]; node2 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> U | <f2> "]; node5 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> N | <f2> "]; node9 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> Y | <f2> "]; node8 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> W | <f2> "]; node10 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> Z | <f2> "]; node7 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> A | <f2> "]; node3 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> G | <f2> "]; "node0":f0 -> "node1":f1; "node0":f2 -> "node2":f1; "node1":f0 -> "node4":f1; "node1":f2 -> "node6":f1; "node4":f0 -> "node7":f1; "node4":f2 -> "node3":f1; "node2":f0 -> "node5":f1; "node2":f2 -> "node9":f1; "node9":f0 -> "node8":f1; "node9":f2 -> "node10":f1; } \end{latex} Finally:: \\begin{latex} \\digraph[scale=0.5]{GraphVizGraph4a} { rankdir = LR; node [shape=record, width=.1, height=.1]; node0 [label = "<p0> | <p1> | <p2> | <p3> | <p4> | | ", height = 3]; node[ width=2 ]; node1 [label = "{<e> r0 | 123 | <p> }" ]; node2 [label = "{<e> r10 | 13 | <p> }" ]; node3 [label = "{<e> r11 | 23 | <p> }" ]; node4 [label = "{<e> r12 | 326 | <p> }" ]; node5 [label = "{<e> r13 | 1f3 | <p> }" ]; node6 [label = "{<e> r20 | 123 | <p> }" ]; node7 [label = "{<e> r40 | b23 | <p> }" ]; node8 [label = "{<e> r41 | 12f | <p> }" ]; node9 [label = "{<e> r42 | 1d3 | <p> }" ]; node0:p0 -> node1:e; node0:p1 -> node2:e; node2:p -> node3:e; node3:p -> node4:e; node4:p -> node5:e; node0:p2 -> node6:e; node0:p4 -> node7:e; node7:p -> node8:e; node8:p -> node9:e; } \\end{latex} Draws a linked list \begin{latex} \digraph[scale=0.5]{GraphVizGraph4a} { rankdir = LR; node [shape=record, width=.1, height=.1]; node0 [label = "<p0> | <p1> | <p2> | <p3> | <p4> | | ", height = 3]; node[ width=2 ]; node1 [label = "{<e> r0 | 123 | <p> }" ]; node2 [label = "{<e> r10 | 13 | <p> }" ]; node3 [label = "{<e> r11 | 23 | <p> }" ]; node4 [label = "{<e> r12 | 326 | <p> }" ]; node5 [label = "{<e> r13 | 1f3 | <p> }" ]; node6 [label = "{<e> r20 | 123 | <p> }" ]; node7 [label = "{<e> r40 | b23 | <p> }" ]; node8 [label = "{<e> r41 | 12f | <p> }" ]; node9 [label = "{<e> r42 | 1d3 | <p> }" ]; node0:p0 -> node1:e; node0:p1 -> node2:e; node2:p -> node3:e; node3:p -> node4:e; node4:p -> node5:e; node0:p2 -> node6:e; node0:p4 -> node7:e; node7:p -> node8:e; node8:p -> node9:e; } \end{latex} I really like this new psfrag stuff! \begin{latex} \psfrag{a10}[cc][cc]{$f^{'}(x)$} \psfrag{b10}[cc][cc]{$\int f^{'}(x)\ dx$} \psfrag{c10}[cc][cc]{$f(x)$} \digraph[scale=1.5]{GraphVizGraph10b}{rankdir=LR; a10->b10; b10->c10} \end{latex}
An Introduction to GraphViz?
By Mihalis Tsoukalos on Wed, 2004-09-08 23:00.
How to use command-line tools and basic GraphViz? utilities to produce graphs both simple and complex.
GraphViz? is a collection of tools for manipulating graph structures and generating graph layouts. Graphs can be either directed or undirected. GraphViz? offers both graphical and command-line tools. A Perl interface also is available, but it is not covered here for reasons of generality. Graphical tools are not going to be discussed in this article either. Instead, this article focuses on using GraphViz? from the command line.
See more here: http://www.wickle.com/wikis/index.php/Graphviz_extension
The format of a GraphViz? command is:
\begin{latex}
\digraph[Options]{Name}{Specification}
\end{latex}
Replace Options with something like scale=1.0 and Specifications
with the actual graph, e.g. a->b; b->c. Replace Name with a name
for your graph.
The LaTeX? extension for GraphViz? (see: LatexTemplate?) produces files
named Name.dot and Name.ps in the images working directory. Since
this graph name is global, it is a good idea to prefix the name with
the name of the page on which the graph occurs.
The follow graphs are generated by MathAction?
My First Graph:
\begin{latex}
\psfrag{alpha}[cc][cc]{$\alpha$}
\psfrag{beta}[cc][cc]{$\beta$}
\psfrag{gamma}[cc][cc]{$\gamma$}
\digraph[scale=0.75]{GraphVizGraph1a}{rankdir=LR; alpha->beta; beta->gamma}
\end{latex}
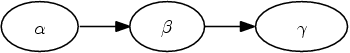 |
A More Complex Example:
\begin{latex}
\digraph[scale=0.8]{GraphVizGraph2a}{
size ="4,4";
main [shape=box]; /* this is a comment */
main -> parse [weight=8];
parse -> execute;
main -> init [style=dotted];
main -> cleanup;
execute -> { make_string; printf}
init -> make_string;
edge [color=red];
main -> printf [style=bold,label="100 times"];
make_string [label="make a string"];
node [shape=box,style=filled,color=".7 .3 1.0"];
execute -> compare;
}
\end{latex}
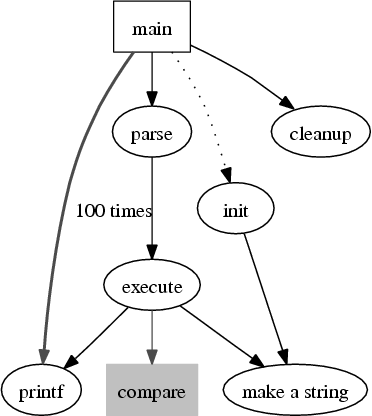 |
Here's One From
http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7275
This:
\begin{latex}
\digraph{GraphVizGraph3a}
{
node [shape = record];
node0 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> J | <f2> "];
node1 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> E | <f2> "];
node4 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> C | <f2> "];
node6 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> I | <f2> "];
node2 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> U | <f2> "];
node5 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> N | <f2> "];
node9 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> Y | <f2> "];
node8 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> W | <f2> "];
node10 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> Z | <f2> "];
node7 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> A | <f2> "];
node3 [ label ="<f0> | <f1> G | <f2> "];
"node0":f0 -> "node1":f1;
"node0":f2 -> "node2":f1;
"node1":f0 -> "node4":f1;
"node1":f2 -> "node6":f1;
"node4":f0 -> "node7":f1;
"node4":f2 -> "node3":f1;
"node2":f0 -> "node5":f1;
"node2":f2 -> "node9":f1;
"node9":f0 -> "node8":f1;
"node9":f2 -> "node10":f1;
}
\end{latex}
 |
Finally:
\begin{latex}
\digraph[scale=0.5]{GraphVizGraph4a}
{
rankdir = LR;
node [shape=record, width=.1, height=.1];
node0 [label = "<p0> | <p1> | <p2> | <p3>
| <p4> | | ", height = 3];
node[ width=2 ];
node1 [label = "{<e> r0 | 123 | <p> }" ];
node2 [label = "{<e> r10 | 13 | <p> }" ];
node3 [label = "{<e> r11 | 23 | <p> }" ];
node4 [label = "{<e> r12 | 326 | <p> }" ];
node5 [label = "{<e> r13 | 1f3 | <p> }" ];
node6 [label = "{<e> r20 | 123 | <p> }" ];
node7 [label = "{<e> r40 | b23 | <p> }" ];
node8 [label = "{<e> r41 | 12f | <p> }" ];
node9 [label = "{<e> r42 | 1d3 | <p> }" ];
node0:p0 -> node1:e;
node0:p1 -> node2:e;
node2:p -> node3:e;
node3:p -> node4:e;
node4:p -> node5:e;
node0:p2 -> node6:e;
node0:p4 -> node7:e;
node7:p -> node8:e;
node8:p -> node9:e;
}
\end{latex}
Draws a linked list
 |
I really like this new psfrag stuff!
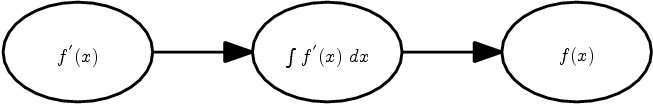 |